Obesity - Obesity Problem, Obesity Cause
Are you suitable for bariatric surgery? | Benefits of Surgery | The vicious cycle of obesity |
Type II DM Control after Bariatric Surgery | Reduction of Cardiovascular Risk after Bariatric Surgery |
Metabolic Syndrome | FAQ
If you consider having a big, round tummy like the Michelin Man as the symbol of fortune, you may need to think otherwise. Obesity not only has a significant impact on your health, it is also associated with a number of chronic illnesses, including type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Currently, there are various laparoscopic bariatric surgeries available for patients suffering from morbid obesity. Together with diet control and altering the absorptive system, weight loss can be achieved with a holistic approach.
What is obesity?
Obesity is resulted by the deposit of excess fats in the body. This is caused by the over absorption and inadequate output of calories. In fact, many people are gaining weight every day due to binge eating, having a fatty diet and lack of exercise. You can find out whether you are overweight by calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI). The BMI is an internationally approved standard in assessing the weight of adults.
The BMI formula is: weight (kg) ÷ (height (m) x height (m))
Click here to calculate your BMI.
Why do we need to treat obesity?
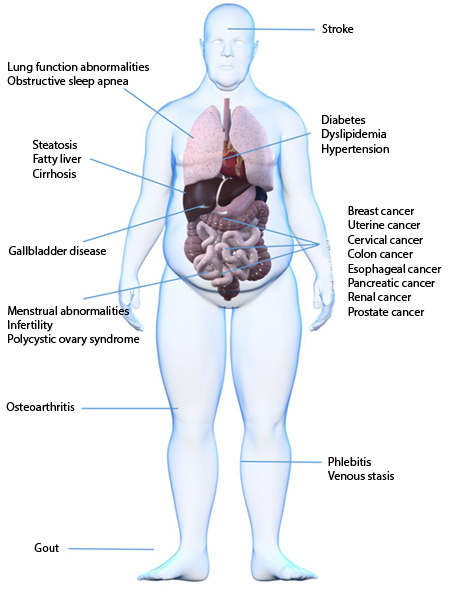
Indeed, obesity does nothing to help you fit into fashionable outfits and affects your appearance and confidence. However, more importantly, it may cause many chronic illnesses that affect your health and may even be fatal. Obesity is associated with diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, ankle degeneration, sleep apnea, hyperlipidemia, as well as menstrual irregularity and hormonal disturbances in women. Central obesity also plays a major role in causing metabolic syndrome, which significantly increases the risk of stroke, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Compared with Caucasians, there are more cases of central obesity among Asians.
Diabetes is another prevalent disease among Asians and should not be ignored. It is associated with numerous complications, including glaucoma and heart diseases. However, most diabetic patients often ignore the problem of obesity, and do not consider obesity as a disease. The problem is often left aside until they realize that medication and insulin injections are still unable to control their blood glucose levels. Many patients will then seek help from their GPs who refer them to specialists for laparoscopic weight loss surgeries.
Having a BMI of 25-29.9 means that patients are overweight, while those with a BMI over 30 are considered as obese. According to APMBSS’s recommendations, laparoscopic bariatric surgery is indicated for Asians with a BMI over 32 who are suffering from diabetes or obesity-related conditions such as hypertension, or those with a BMI over 37.
Various weight loss methods:
Exercise and dietary control are the basic fundamentals of weight loss. Under suitable conditions, certain patients could also take prescribed medication to reach a healthy weight. However, for those between ages 18 and 65 who cannot consistently lose weight even by taking medication, following nutritionists’ advice and doing exercise, as well as those with a BMI over 37, or those with a BMI over 32 who are suffering from diabetes or obesity-related conditions, laparoscopic bariatric surgery may be the way to go. This includes laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, laparoscopic gastric plication and laparoscopic gastric bypass, as well as a procedure known as intragastric balloon. Patients under the age of 18 may also undergo the above surgeries with doctor’s approval.


