Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass
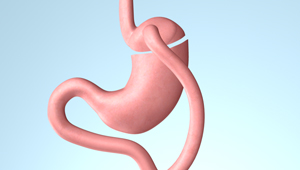
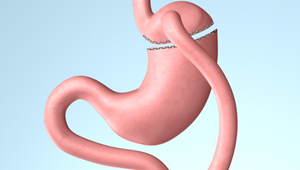
Gastric bypass is by far the most effective weight loss surgery for obese as well as diabetic patients with a success rate of over 80%. Gastric bypass is a combination of restrictive and malabsorptive weight loss surgeries. It reduces stomach volume and appetite while bypassing the duodenum to reduce calorie absorption in order to achieve significant weight loss. However, patients are required to take vitamins regularly and undergo regular checkups to prevent the risk of anemia.
Procedure of Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass
Laparoscopic gastric bypass is suitable for patients with a BMI over 40. A liquid diet is suggested two weeks before the surgery. No food is allowed on the day before the surgery. Performed under general anesthesia, 4 to 5 small incisions will be made on the abdomen, each being 1-2 cm in diameter, so that laparoscopic instruments could be inserted. Gastrectomy will then be performed to reduce stomach volume by 20-30ml.
The ileum will then be connected to the stomach, bypassing the duodenum. The remaining part of the stomach will remain in the body for secreting gastric juices for iron and calcium absorption. The surgery takes around 2-3 hours. Patients have to be hospitalized for 4-5 days but may move around after surgery. Patients are advised to maintain a liquid diet for the first two weeks after surgery, and then progress to a puree diet. One month later, normal diet can be resumed. However, patients need to follow dietitians’ advice and exercise regularly, as well as undergo regular follow ups for effective weight loss.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass
- Effective diabetic treatment: gastrectomy affects hormone secretion in the body. Therefore, around 80% of patients have their diabetes cured after the surgery. It is also effective in managing hypertension, hyperlipidemia and sleep apnea.
- Effective weight loss: this surgery is by far the best laparoscopic weight loss surgery.
- Quick recovery: laparoscopic surgery is relatively less traumatic and allows quicker recovery.
Risks of Gastric Bypass
- Lack of vitamins: gastric bypass affects absorption in the small intestines. As chronic vitamin deficiency may lead to anemia, patients are required to take vitamin supplements and undergo regular checkups to screen for anemia and malnutrition.
- Complications: this is a relatively complicated surgery. The risk of complications is about 1%. Therefore, it is highly advisable to have the surgery performed by experienced surgeons.
- Not suitable for upper endoscopy: since the majority of the stomach and duodenum are bypassed, endoscopy cannot be used for examination.
The information on this website is for general educational purpose only.
Readers should consult their physician before considering treatment, and should not interpret their condition solely based on the information above.


